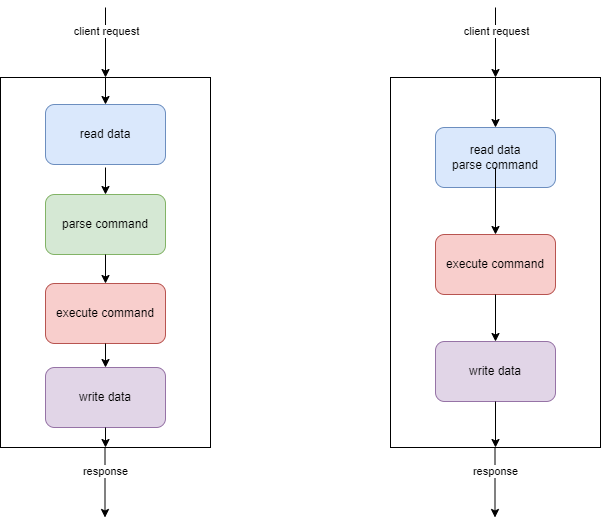
In BioServer, the steps of request process are:
- read data from socket
- parse data to a command
- execute the command
- write data to socket
As parse data is quite simple, so we can merge it to read data.
in such case, we are able to use multiple threads to handle each step.
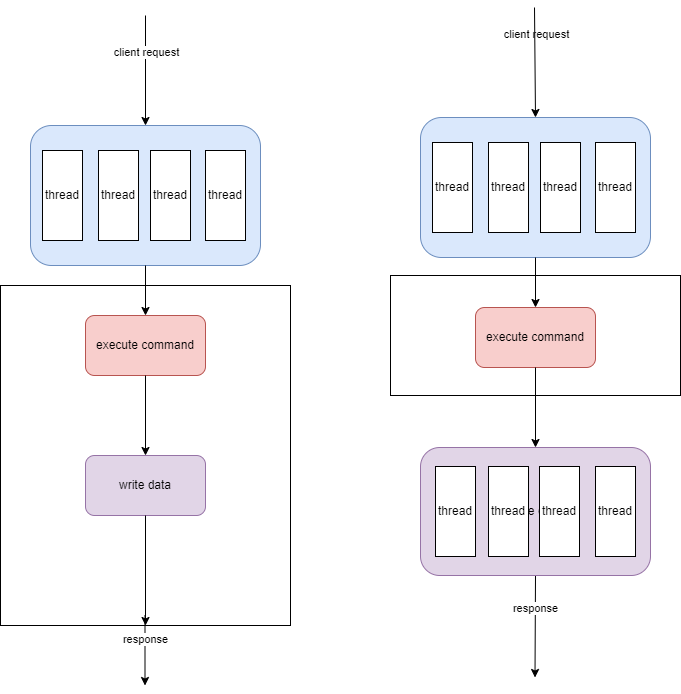
So MultiThreadNioServer is implemented.
public class MultiThreadNioServer extends AbstractNioServer {
@Override
protected void process(Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator) throws IOException {
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next();
if (selectionKey.isAcceptable()) {
registerReadOperation(selectionKey);
} else if (selectionKey.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
selectionKey.cancel();
process(socketChannel);
}
iterator.remove();
}
handleClients(false);
}
@Override
protected void process(SocketChannel socketChannel) {
executorService.submit(() -> {
Client client = new Client(socketChannel);
MeasureData measureData = new MeasureData();
client.setMeasureData(measureData);
try {
measureData.add(RequestMeasureCollector.FIELD_NAME_CONNECTED);
DataReader dataReader = new ChannelDataReader(socketChannel, bufSize, MAX_COMMAND_LENGTH);
List<ByteWord> words = commandReader.read(dataReader);
measureData.add(RequestMeasureCollector.FIELD_NAME_READ);
Command command = CommandFactory.parseCommand(words);
measureData.add(RequestMeasureCollector.FIELD_NAME_PARSE);
client.setCommand(command);
} catch (JimdsException e) {
client.setClientError(true);
measureData.add(RequestMeasureCollector.FIELD_NAME_ERROR);
// internal exception, write to output
NetworkData data = new NetworkError(e.getMessage());
client.setResult(data);
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Throwable e) {
client.setClientError(true);
measureData.add(RequestMeasureCollector.FIELD_NAME_ERROR);
// should only be thrown when writing data to output
// if input throws IOException, an error message will be written to output.
// throw new RuntimeException(e);
// ignore the message, and close socket
e.printStackTrace();
}
queue.offer(client);
});
}
}
In method process() all actions are executed in ExecutorService. After a command is parsed, the data is put into a queue, and the method handleClients will process the queue in main thread.
public class MultiThreadNioServer extends AbstractNioServer {
/**
* Handle all clients in queue.
*
* @param forceSync whether to handle clients synchronized
*/
private void handleClients(boolean forceSync) {
List<Client> clients = new ArrayList<>();
// only process clients in queue currently.
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
clients.add(queue.poll());
}
for (Client client : clients) {
if (client.isClientError()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = client.getSocketChannel();
if (socketChannel.isOpen()) {
NetworkData data = client.getResult();
if (data == null) {
data = new NetworkError("Error");
}
writeData(data, socketChannel, true);
}
} else {
executeCommand(client);
if (!forceSync && writeAsync) {
executorService.submit(() -> {
writeData(client.getResult(), client.getSocketChannel(), true);
});
} else {
writeData(client.getResult(), client.getSocketChannel(), true);
}
}
}
}
}
Notices that it’s optional to write data async. and if it’s async, the operation is put into the same ExecutorService.